Tous les drapeaux . XYZ
Tous les drapeaux . XYZ

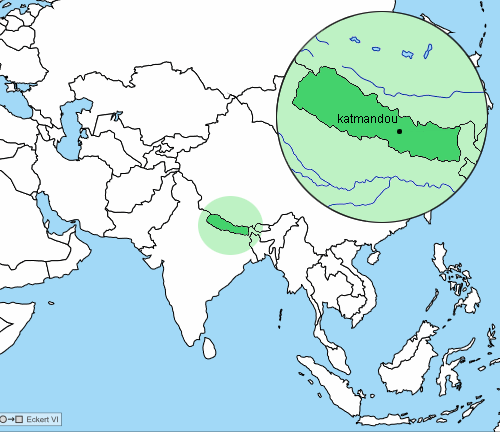
| Capitale : Katmandou |
| Superficie : 147 179 km2 (93e) |
| Population : 29 384 297 hab. (2017) |
| Monnaie : Roupie népalaise |
| Indépendance : 1768 |
| Ratio | 5/4 |
| Grille FIAV |  |
| Fonction |  |
 |
Le drapeau de la république démocratique fédérale du Népal est composé de deux triangles superposés. C’est le seul drapeau national en activité qui n’est pas rectangulaire.
Ce drapeau a un fond rouge avec une bordure bleue. Le triangle supérieur est frappé d’un demi-soleil au-dessus d’un croissant de lune ouvert vers le haut.
Le triangle inférieur est frappé d’un soleil à douze rayons légèrement plus grand.
• Les deux triangles représentent l’Himalaya mais symbolisent également le bouddhisme et l’hindouisme.
• La couleur rouge (rouge carmin) est la couleur du Népal.
• Le drapeau supérieur avec un croissant de lune et le soleil en berceau représente la famille royale.
• La partie inférieure représente la famille des Premiers ministres (poste occupé de façon héréditaire par la famille Rana).
Les représentations humaines des premiers drapeaux se sont simplifiées devenir finalement des soleils.




Le royaume de Mustang est une petite région de l’Himalaya frontalière avec la Chine d’environ 2 000 km2. Il a existé entre 1380 et 1951 et forme maintenant le district de Mustang intégré au Népal.
Le drapeau reprend les couleurs du Népal avec au centre un soleil à 16 rayons.

Le Népal est le seul pays à avoir défini mathématiquement son drapeau. Il s’agit de l’annexe 1 de sa constitution.
Ci-dessous sa traduction.
ANNEXE 1 : Méthode de fabrication du drapeau national du Népal (EN RELATION AVEC LA CLAUSE (2) DE L’ARTICLE 8)
(1) Sur la partie inférieure d’un tissu cramoisi, tracer une ligne AB de la longueur requise de gauche à droite.
(2) Depuis A, tracer une ligne AC perpendiculaire à AB, en faisant AC égal à AB plus un tiers de AB. À partir de AC, marquer D de manière que la ligne AD soit égale à AB. Relier B et D.
(3) Depuis BD, marquer E de manière que BE soit égal à AB.
(4) En passant par E, tracer une ligne FG à partir du point F sur AC, parallèle à AB vers la droite. Marquer FG égal à AB.
(5) Relier C et G.
(6) Depuis AB, marquer AH de manière que AH soit égal au quart de AB, et à partir de H tracer une ligne HI parallèle à AC, touchant CG en I.
(7) Bisecter CF en J et tracer une ligne JK parallèle à AB, touchant CG en K.
(8) Soit L le point où les lignes JK et HI se coupent.
(9) Relier J et G.
(10) Soit M le point où JG et HI se coupent.
(11) Avec pour centre M et le rayon égal à la distance la plus courte de M à BD, marquer N sur la partie inférieure de HI.
(12) En partant de O, un point sur AC et en passant par M, tracer une ligne de gauche à droite parallèle à AB.
(13) Avec pour centre L et rayon LN, tracer un demi-cercle sur la partie inférieure ; que P et Q soient les points où il touche la ligne OM.
(14) Avec pour centre M et rayon MQ, tracer un demi-cercle sur la partie inférieure touchant P et Q.
(15) Avec pour centre N et rayon NM, tracer un arc touchant PNQ en R et S. Relier R et S. Soit T le point où RS et HI se coupent.
(16) Avec pour centre T et rayon TS, tracer un demi-cercle sur la partie supérieure de PNQ, touchant en deux points.
(17) Avec pour centre T et rayon TM, tracer un arc sur la partie supérieure de PNQ, touchant en deux points.
(18) Huit triangles égaux et similaires représentant la lune doivent être créés dans l’espace compris à l’intérieur du demi-cercle du point (16) et à l’extérieur de l’arc du point (17).
(19) Bisecter la ligne AF en U, et tracer une ligne UV parallèle à AB, touchant BE en V.
(20) Avec pour centre W, le point où HI et UN se coupent, et rayon MN, tracer un cercle.
(21) Avec pour centre W et rayon LN, tracer un cercle.
(22) Douze triangles égaux et similaires représentant le soleil doivent être créés dans l’espace compris entre les cercles des points (20) et (21), avec les deux sommets de deux triangles touchant la ligne HI.
(23) La largeur de la bordure sera égale à la largeur TN. Elle sera de couleur bleu foncé et sera appliquée sur tous les côtés du drapeau. Cependant, aux angles du drapeau, les angles externes seront égaux aux angles internes.
(24) La bordure mentionnée ci-dessus sera appliquée si le drapeau est utilisé avec une corde. Par contre, si le drapeau doit être hissé sur un mât, le trou sur la bordure du côté AC pourra être prolongé selon les besoins.
Explication : Les lignes HI, RS, FE, ED, JG, OQ, JK et UV sont imaginaires.
De même, les cercles externes et internes du soleil ainsi que les autres arcs, à l’exception du croissant de lune, sont imaginaires. Ils ne sont pas représentés sur le drapeau.

